Setup FTP Container
Prerequisites¶
- VirtualBox or VMware Workstation Pro Installed.
- Virtual Machine
[project-x-corp-svr]is configured with Docker.
Network Topology¶
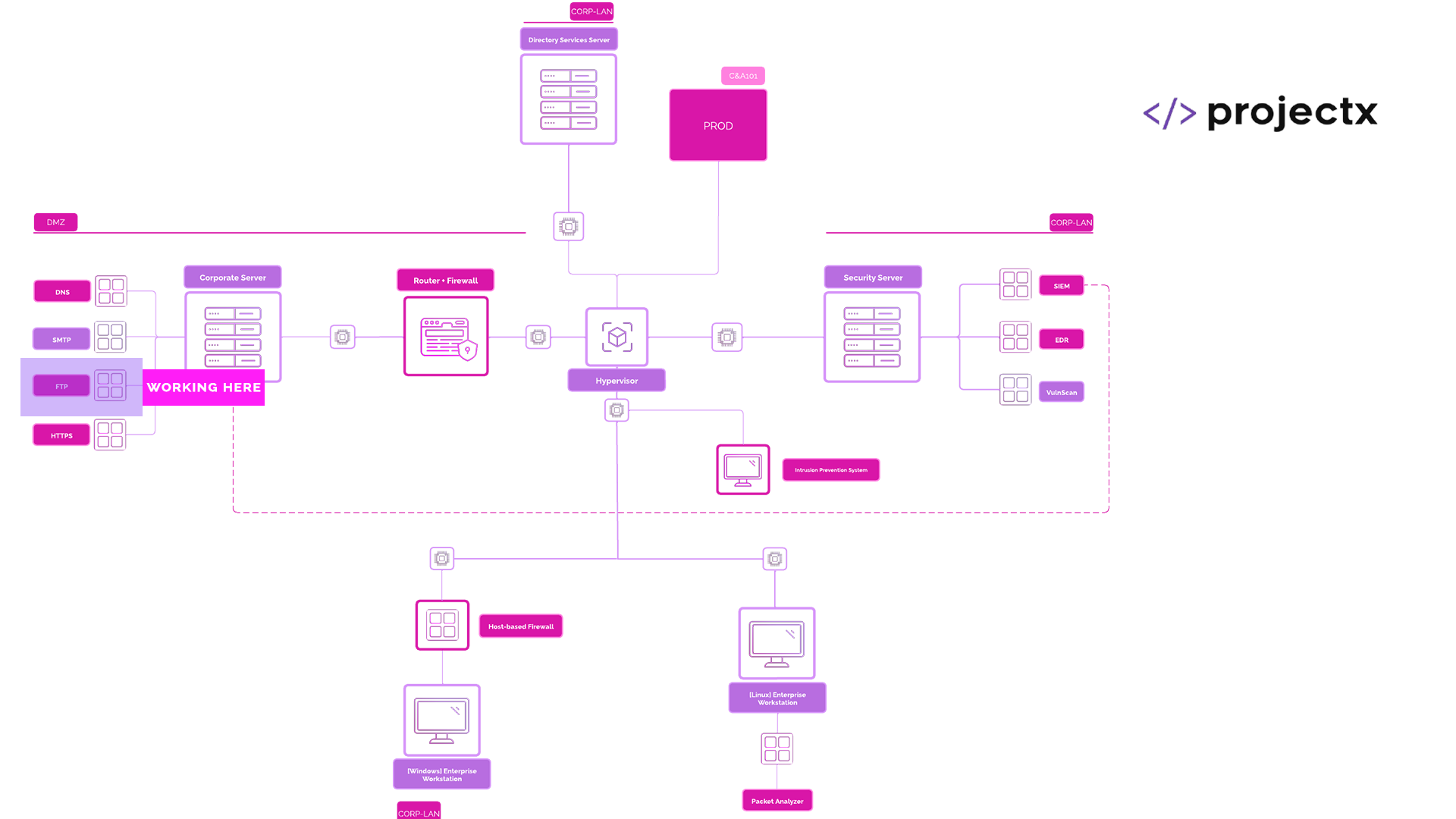
FTP Servers Overview¶
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol used to transfer files between a client and server. FTP servers can be used to store, retrieve, and facilitate access control to sensitive files.
We will be using vsftp, which is a common FTP server implementation used to host and store files.
What is FTP?¶
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files between a client and server over a TCP/IP network. It allows users to upload, download, rename, delete, and manage files on remote servers.
How is FTP used?¶
FTP and FTP servers are commonly used to upload website files, store internal documents, back up data to remote location, and automate file transfers.
FTP is mostly a technology of the past. You will see disparate uses, depending on the scale and age of the network.
FTP still provides a great platform to learn about network protocols.
Security Implications¶
Due to its age and legacy, FTP has a few security callouts.
By default FTP transmits data in plaintext, including usernames and passwords. It also can be misconfigured to allow anyone to access, called anonymous access, to open and retrieve files.
Configure vsftp Container¶
💡 Note: This may be a bit finicky, given this is a very old version of vsftp, we've found its had issues while running the exploit.
Open a new terminal session.
Navigate to the home directory: cd /home.
Let's create a new folder called ftp: mkdir ftp.
Create a new Dockerfile: nano Dockerfile.
Inside this Dockerfile we will use Ubuntu 18.04 as our base image, install vsftp dependencies as well as a few useful networking tools, exposing port 21 and 6200.
FROM ubuntu:18.04
# Avoid interactive prompts during package install
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
# Install necessary dependencies for vsftpd build & debug
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
git \
wget \
nano \
curl \
netcat \
xinetd \
gcc \
make \
libpam0g-dev \
libssl-dev \
iputils-ping \
iproute2 \
tcpdump \
iptables \
vim \
strace \
lsof
# Create a working directory
WORKDIR /workspace
# Open port 21 for FTP and 6200 - will be used for exploit.
EXPOSE 21 6200
# Default to an interactive shell
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
Let's build a new image from the Dockerfile.
docker build -t project-x-image-ftp ..
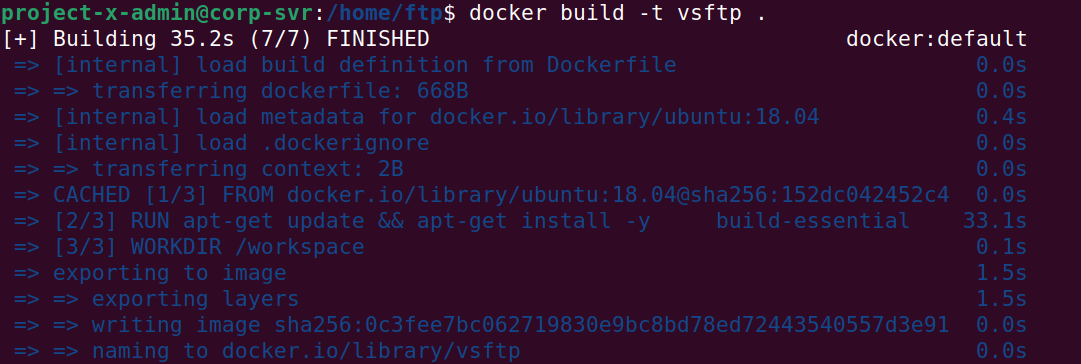
We can run the container and automatically login.
docker run -it --network host --name ftp-svr projectx-image-ftp.

You will now be logged into the new container. By default, we are the root user.
Let's now setup vsftpd-2.3.4.
♥ Huge kudos goes to Doctor Kisow for the Github repository, we are reproducing his exercise. Full credit goes to him.
- https://github.com/DoctorKisow/vsftpd-2.3.4/tree/master
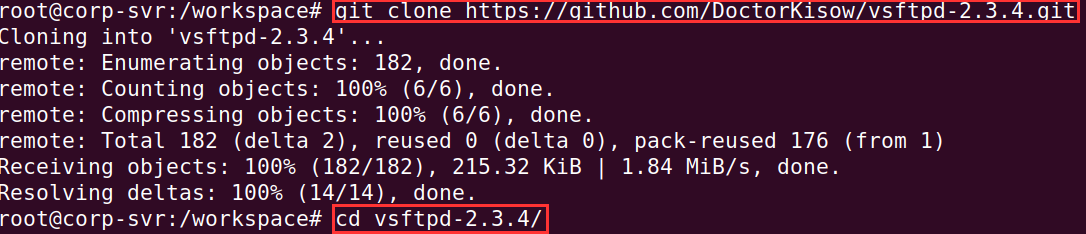
Clone the modified vsftpd-2.3.4.git repository.
git https://github.com/DoctorKisow/vsftpd-2.3.4.git
Change directories into the folder.
cd vsftpd-2.3.4
If you perform an ls you can see all the configuration files.
Change the vsf_findlibs.sh permissions to executable.
chmod +x vsf_findlibs.sh

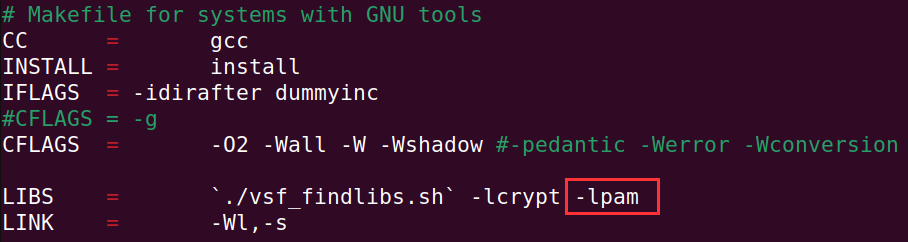
Open the Makefile. Add -lpam to the end of the LIBs line. Make sure there is a space in between.

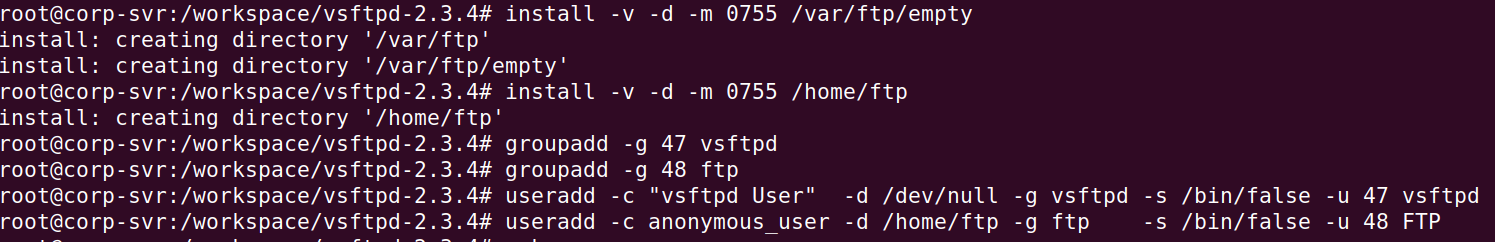
Add the following commands to adjust vsftp settings.
install -v -d -m 0755 /var/ftp/empty
install -v -d -m 0755 /home/ftp
groupadd -g 47 vsftpd
groupadd -g 48 ftp
useradd -c "vsftpd User" -d /dev/null -g vsftpd -s /bin/false -u 47 vsftpd
useradd -c anonymous_user -d /home/ftp -g ftp -s /bin/false -u 48 FTP
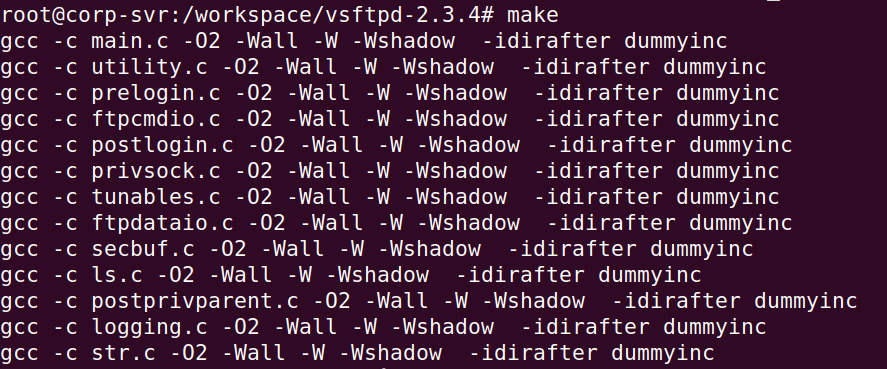
Use the make command to create the vsftpd ELF executable.
make
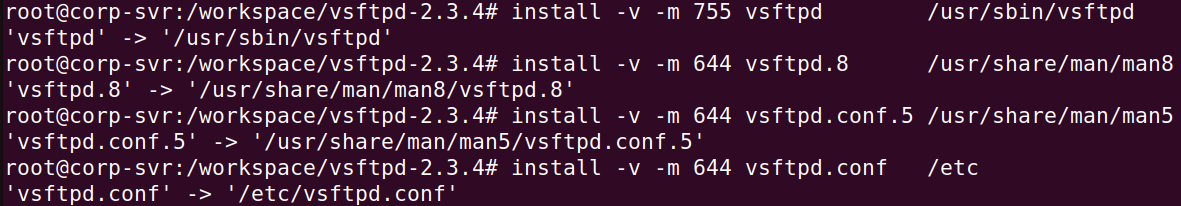
Add a few symlinks to the container's file system.
install -v -m 755 vsftpd /usr/sbin/vsftpd
install -v -m 644 vsftpd.8 /usr/share/man/man8
install -v -m 644 vsftpd.conf.5 /usr/share/man/man5
install -v -m 644 vsftpd.conf /etc
Add a new user ftp and add the ftp user to the ftp group.
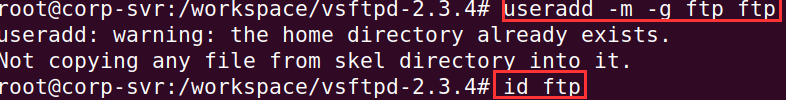
Create new directory called /usr/share/empty and add exectuable permissions.
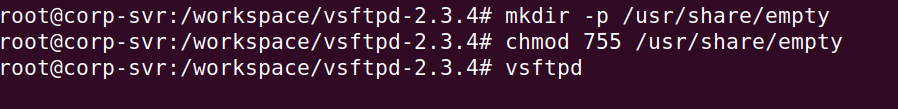
We can now run the vsftpd service. You will see a blank screen. You can exit out of the service with CTRL + C.

Open another terminal session tab, we should now be on our [project-x-corp-svr] terminal.
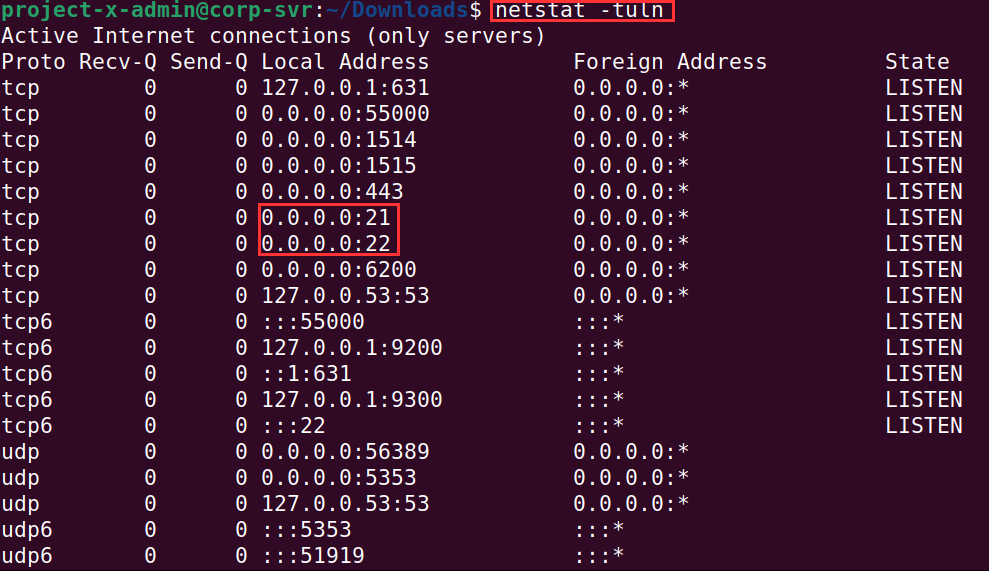
Supply netstat -tuln.
You can see ports 20 and 21 are enabled, listening on all IP addresses.
To exit out of the container, we can supply exit.
We will be able to re-run the same container when it comes time to provision an exploit.
docker start ftp-svr.
📷 Take Snapshot!